EEPROM機能のエミュレーション
EEPROM(電源が供給されて、読み取り - 書き込み可能なメモリ)は、ユーザーが変更できるメモリ(ROM)には、通常よりも高い電圧に削除と再プログラミング(再書き込み)を行うことができます。
エミュレーション原理
このシステムは、独自のファイルシステムがあるLinuxベースで保存されたデータをNorFlashに記録されます(削除回数が100,000回以上、Nandfalshがありません。NandFlashは不良ブロックが発生した後、様々なリスクが発生する可能性があります)。 /dataパーティションは、ユーザーデータのためにFlywizOS内部に予約されています。マイクロコントローラの動作に慣れているユーザーの便宜のために /dataパーティションの下にファイルを作成して、EEPROM空間をシミュレートします。(/dataパーティションのサイズは、特定のシステムのバージョンに応じて、1Mまたは数百KBの範囲)
使用シナリオ
電源がオフの状態でデータを保持します。
実装段階
まず、プロジェクトの jniディレクトリにヘッダファイルを作成します。
プロジェクトでjniを選択し、マウスの右ボタンをクリックして、ポップアップコンテキストメニューからNew -> Header Fileオプションを選択し、名前をvireeprom.hと指定して、[Finish]をクリックします。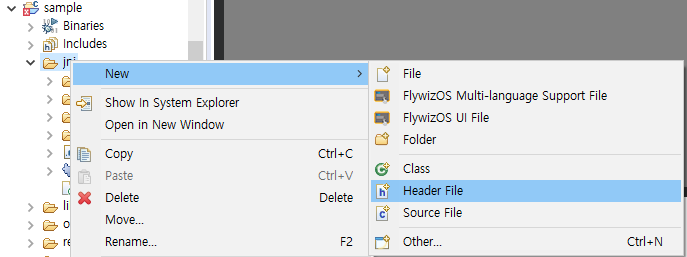
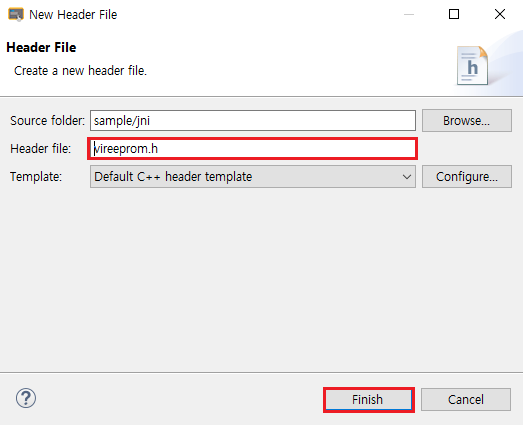
追加したばかりのヘッダーファイルに次のコードをコピーします。(ヘッダファイルの作成時に、いくつかの内容が自動的に追加および削除することができます。)
このコードは、EEPROMのエミュレーション機能を実装します。#ifndef JNI_VIREEPROM_H_ #define JNI_VIREEPROM_H_ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> /** * The storage size of the emulated EEPROM, in bytes, it is recommended not to be too large */ #define EEPROM_SIZE 1024 /** * Actually saved as a file /data/eeprom.eep */ #define EEPROM_FILE "/data/eeprom.eep" class VirEEPROM { public: VirEEPROM() { memset(buff_, 0, sizeof(buff_)); file_ = fopen(EEPROM_FILE, "rb+"); if (file_) { fread(buff_, 1, EEPROM_SIZE, file_); fseek(file_, 0, SEEK_END); int f_size = ftell(file_); //Adjust the file to a suitable size if (f_size != sizeof(buff_)) { ftruncate(fileno(file_), sizeof(buff_)); fseek(file_, 0, SEEK_SET); fwrite(buff_, 1, sizeof(buff_), file_); fflush(file_); sync(); } } else { file_ = fopen(EEPROM_FILE, "wb+"); //Adjust the file to a suitable size ftruncate(fileno(file_), sizeof(buff_)); } } virtual ~VirEEPROM() { if (file_) { fflush(file_); fclose(file_); sync(); } } /** * Return : less than 0 is failure, greater than 0 is the actual number of bytes written * Parameter: The data pointer that value needs to save, which can be a structure pointer, char*, int*..., size is the * size of the data to be saved * Examples of use: * const char buff[]="12345678"; * VIREEPROM->WriteEEPROM(0,buff,sizeof(buff); */ int Write(int addr, const void* value, int size) { if (file_ == NULL) { return -1; } if ((addr >= EEPROM_SIZE) || ((addr + size) > EEPROM_SIZE)) { //Oversize return -2; } memcpy(buff_ + addr, value, size); if (0 != fseek(file_, addr, SEEK_SET)) { return -3; } int n = fwrite((char*)value, 1, size, file_); fflush(file_); sync(); return n; } /** * Return : less than 0 is a failure, greater than 0 is the number of bytes actually read * Parameter: the data pointer to be read by value, which can be a structure pointer, char*, int*..., size is the size of * the data to be read * Examples of use: * char buff[9]; * VIREEPROM->ReadEEPROM(0,buff,sizeof(buff); */ int Read(int addr,void* value,int size) { if (file_ == NULL) { return -1; } if ((addr >= EEPROM_SIZE) || ((addr + size) > EEPROM_SIZE)) { //Oversize return -2; } memcpy(value, buff_ + addr, size); return size; } /** * Return: * 0 Success * Less than 0 failed */ int Erase() { if (file_ == NULL) { return -1; } if (0 != fseek(file_, 0, SEEK_SET)) { return -2; } memset(buff_, 0, sizeof(buff_)); if (sizeof(buff_) != fwrite(buff_, 1, sizeof(buff_), file_)) { return -3; } fflush(file_); sync(); return 0; } static VirEEPROM* getInstance() { static VirEEPROM singleton; return &singleton; } private: unsigned char buff_[EEPROM_SIZE]; FILE* file_; }; #define VIREEPROM VirEEPROM::getInstance() #endif /* JNI_VIREEPROM_H_ */今までの準備作業が完了したので、正常であるかをテストするために、いくつかの例を作成します。
mainLogic.ccソースファイルを開き、ファイルの先頭にある "vireeprom.h"ヘッダファイルをインクルードしてください。#include "vireeprom.h"Test code
static void onUI_init(){ //The value array, starting from address 0, is written sequentially char value[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4}; VIREEPROM->Write(0, value, sizeof(value)); //Start reading from address 0, read 4 bytes in sequence, and save the read content in buf char buf[4] = {0}; VIREEPROM->Read(0, buf, sizeof(buf)); //Output log LOGD("Data read : %02x, %02x, %02x, %02x", buf[0], buf[1], buf[2], buf[3]); //Clear all eeprom to 0 VIREEPROM->Erase(); }