Socket network programming
If you are familiar with Linux socket programming, you can perform network programming according to the standard Linux socket programming interface.
Implement operations for some commonly used socket programming, for example, create a TCP client, We have made a simple package based on the standard interface of Linux, which is convenient to use. If necessary, you can follow the steps to integrate the source code into your own project.
Porting steps
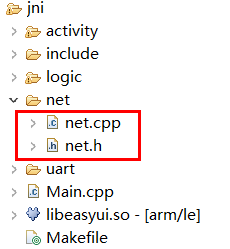
- Create a new folder under the project's jni folder and name it
net
How to use
TCP Client
- Required header file
#include "net/net.h" - Example
//Use TCP protocol to connect to port 80 of the domain name www.baidu.com, and change the domain name to IP. net::Conn* conn = net::Dial("tcp", "www.google.com:80"); //net::Conn* conn = net::Dial("tcp", "14.215.177.38:80"); if (conn) { byte buf[2048] = {0}; const char* req = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n"; //send conn->Write((byte*)req, strlen(req)); while (true) { //read,1000ms timeout int n = conn->Read(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 1000); if (n > 0) { buf[n] = 0; LOGD("read %d bytes: %s", n, buf); } else if (n == 0) { LOGD("Normal disconnection"); break; } else if (n == net::E_TIMEOUT) { LOGD("read timeout"); } else { LOGD("error"); break; } } //Close the connection conn->Close(); //Release memory delete conn; conn = NULL;
UDP Client
- Required header file
#include "net/net.h" - Example
//Use udp protocol to connect IP: 192.168.1.100 port 8080 net::Conn* conn = net::Dial("udp", "192.168.1.100:8080"); if (conn) { byte buf[2048] = {0}; const char* req = "hello"; conn->Write((byte*)req, strlen(req)); while (true) { //read,1000ms timeout int n = conn->Read(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 1000); if (n > 0) { buf[n] = 0; LOGD("read %d bytes: %s", n, buf); } else if (n == 0) { LOGD("Normal disconnection"); break; } else if (n == net::E_TIMEOUT) { LOGD("read timeout"); //Set timeout here to exit break; } else { LOGD("error"); break; } } //Close the connection conn->Close(); //Release memory delete conn; conn = NULL; }